Dr Ansar Ahamed( Otorhinolaryngologist)
Introduction
Acute Suppurative Otitis Media (ASOM) is a prevalent condition among children that requires parents’ understanding and attention.
This article aims to shed light on the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures associated with ASOM.
I. Understanding Acute Suppurative Otitis Media (ASOM)
ASOM, also known as a middle ear infection, is an inflammatory condition affecting the middle ear.
The prevalence of ASOM among children is significant, with studies indicating that up to 75% of children experience at least one episode of ASOM before the age of 3.
II. What Causes Acute Suppurative Otitis Media?
Role of bacteria in ASOM
Bacterial infection plays a critical role in ASOM. Pathogenic bacteria often invade the middle ear through the Eustachian tube, leading to inflammation and the accumulation of fluid or pus behind the eardrum.
These pathogenic bacteria are
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Haemophilus influenza
- Moraxella catarrhalis
Factors contributing to the development of ASOM
Several factors can contribute to the development of ASOM.
These may include a
- Weakened immune system
- Colds or respiratory infections
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
- Daycare attendance
- Bottle-feeding in a supine position
Understanding these factors can help parents take proactive measures toward prevention.
III. Signs and Symptoms of Acute Suppurative Otitis Media
Ear pain: The primary symptom
Ear pain is the hallmark symptom of ASOM and often the first indication that something is amiss.
Children may express their discomfort by tugging, pulling, or rubbing their ears.
It is crucial to initiate proper care and seek medical attention promptly to alleviate the pain.
Other common symptoms
In addition to ear pain, other symptoms may manifest in children with ASOM.
These can include
- Fever
- Irritability
- Poor appetite
- Difficulty sleeping
- Decreased hearing
- Drainage of fluid
- Pus from the affected ear
Vigilance in observing these symptoms can aid in early detection and treatment.
Fever and irritability
A fever is a common response to an infection and can accompany ASOM.
It is essential for parents to monitor their child’s body temperature and consult a healthcare professional if the fever persists or reaches a high level.
Irritability can also be a manifestation of a child’s discomfort and should not be overlooked.
Hearing loss and drainage
The accumulation of fluid or pus behind the eardrum can lead to temporary hearing loss.
This hearing impairment can affect a child’s language and cognitive development.
With severe cases, the fluid may drain out of the ear, indicating a rupture of the eardrum and the need for immediate medical attention.
IV. Diagnosing Acute Suppurative Otitis Media

To diagnose ASOM accurately, a healthcare provider will conduct a thorough examination of the ear using an otoscope. This handheld instrument allows visualization of the ear canal, eardrum, and any signs of inflammation or fluid build-up.
Clinical findings
The ear finding will depend on the present stage and findings may vary according to disease progression.
Stage of tubal occlusion
- Prominent lateral process of malleus
- Loss of cone of light
Stage of presuppuration
Tympanic membrane is congested and may have cart wheel appearance
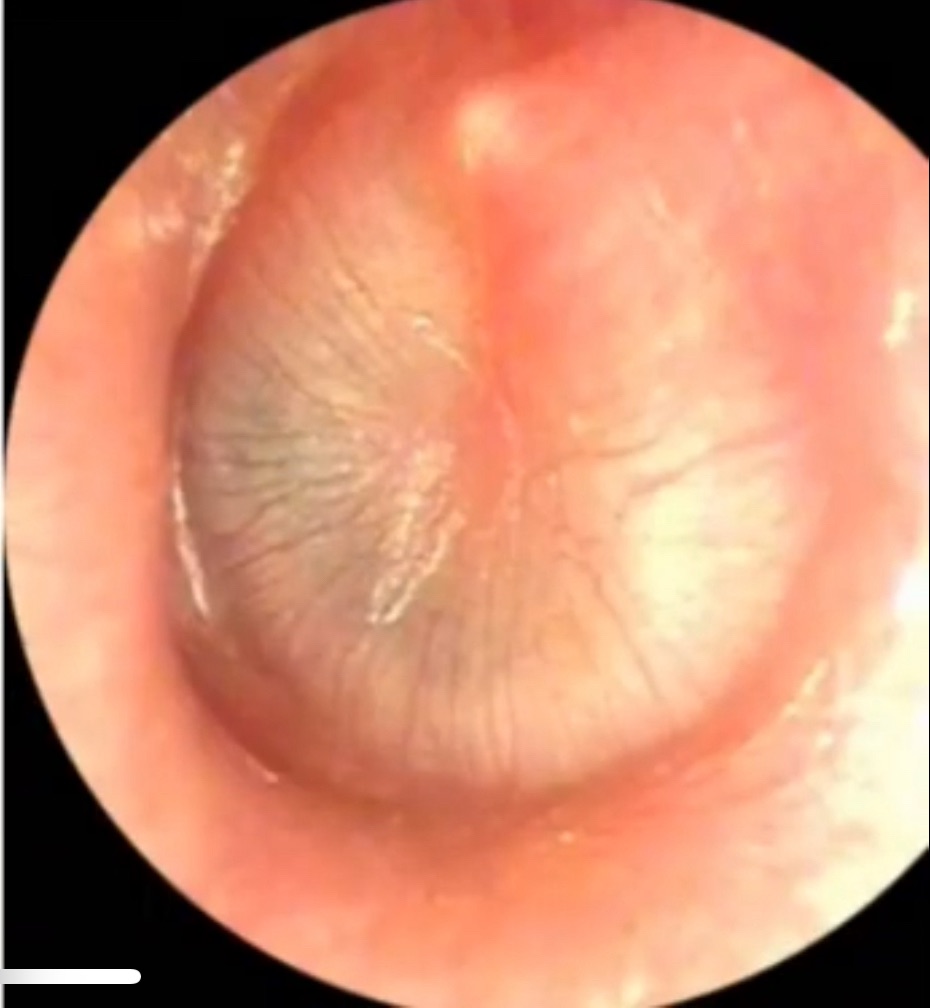
Stage of suppuration
Bulging tympanic membrane is seen
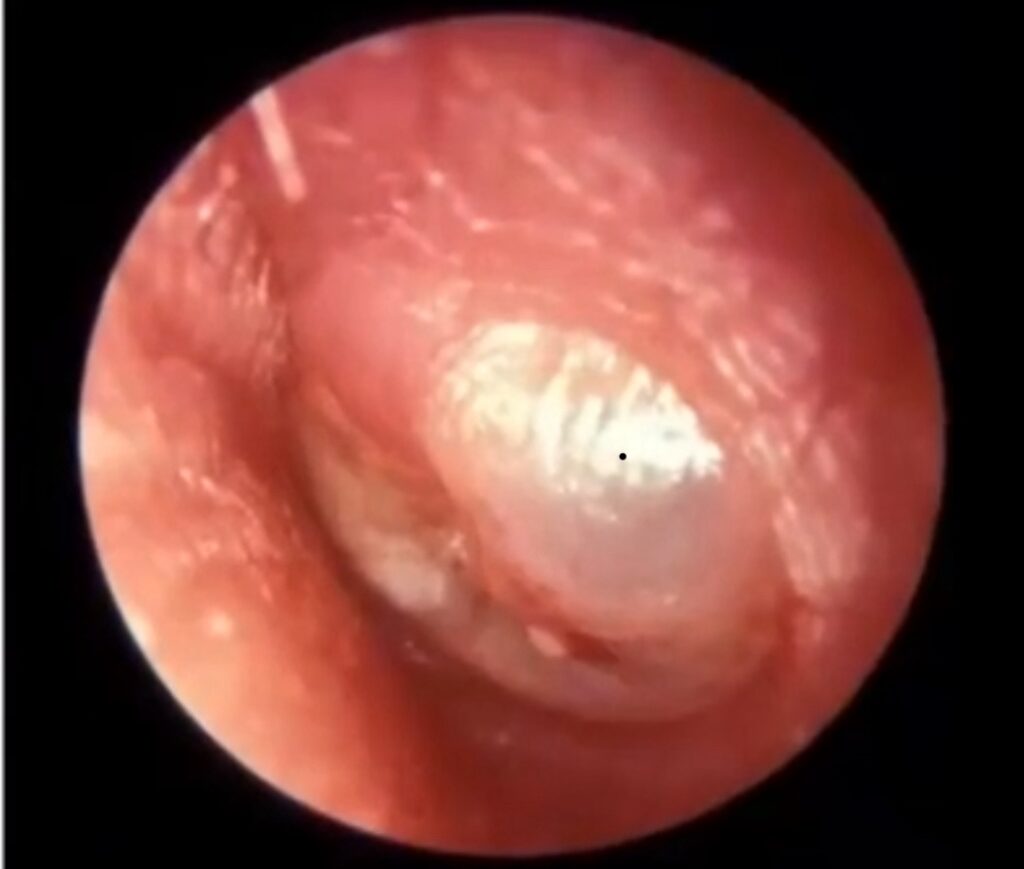
Stage of resolution
- Mucopurulent discharge may be seen in external auditory canal
- A small perforation may be seen in the ear drum

Additional tests, such as a tympanometry, may be performed to assess the mobility and condition of the eardrum.
V. Understanding Middle Ear Anatomy

To better understand ASOM, it is important to comprehend the intricate workings of the middle ear.
The middle ear is a small, air-filled chamber located behind the eardrum.
It consists of the ossicles (tiny bones), which transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear.
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the throat, facilitating equalization of pressure and drainage of fluids.
VI. Age Factors and Risk Groups
ASOM prevalence based on age
ASOM can affect individuals of any age; however, it is more commonly observed in young children.
This is primarily due to the relatively horizontal position of their Eustachian tubes, making it easier for bacteria to ascend and cause infection.
As children grow, the angle of the Eustachian tube gradually changes, reducing the risk of ASOM.
Groups prone to ASOM
Certain groups are more prone to ASOM.
Those who may be at higher risk are
- Children attending daycare centers
- Those exposed to secondhand smoke
- Individuals with a family history of ASOM
- Those with anatomical abnormalities of the Eustachian tube or cleft palate
Recognizing these risk factors can prompt parents to undertake preventive strategies and seek prompt medical attention.
VII. Preventive Measures for Acute Suppurative Otitis Media
Vaccinations and their significance

Vaccinations play a crucial role in preventing ASOM.
Immunizations against bacteria responsible for ASOM, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae type B, can significantly reduce the incidence of infections and subsequent complications.
Keep vaccinations up to date as it can help prevent infections that can lead to acute suppurative otitis media.
Vaccinations, such as
- Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV)
- Annual influenza vaccine
Consult with a healthcare provider to ensure your child is up-to-date on recommended vaccinations.
Promoting good hygiene practices
Encouraging good hygiene practices can help reduce the risk of ASOM.
Prevention and Management of Recurrent Acute Suppurative Otitis Media
Preventing acute suppurative otitis media is a key consideration, particularly for individuals who are prone to recurrent infections.
Here are some practical prevention strategies to reduce the risk:
1. Maintain good hand hygiene: Regularly washing hands with soap and water, especially before eating or touching the face, can help minimize the spread of bacteria and viruses.
2. Avoid exposure to cigarette smoke: Passive smoking increases the risk of ear infections, so it’s crucial to avoid exposure to secondhand smoke.
3. Breastfeed infants: Breast milk contains antibodies that can help strengthen the immune system and protect against infections, including acute suppurative otitis media. If breastfeeding is not an option, consult with a healthcare professional about appropriate infant formulas.
5. Practice good respiratory hygiene: Covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, using tissues or elbows, can help reduce the spread of respiratory pathogens.
6. Avoid sharing personal items: Sharing items such as towels, earphones, or utensils can increase the risk of infection transmission. Encourage each family member to have their own personal items.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of acquiring acute suppurative otitis media, especially in vulnerable populations such as children.
Home Remedies for Acute Suppurative Otitis Media
In addition to medical treatment, certain home remedies can provide relief for individuals with acute suppurative otitis media.
It is important to note that these remedies should not replace medical advice and should be used in conjunction with professional care.
Here are some home remedies that may help alleviate symptoms:
1. Warm compress: Applying a warm compress to the affected ear can help reduce pain and discomfort. Ensure the compress is not too hot to avoid burns.
2. Elevation: Sleeping with the affected ear elevated can help promote drainage and relieve pressure.
3. Saltwater gargle: Gargling with warm saltwater can help soothe the throat and alleviate associated symptoms.
4. Hydration: Staying hydrated can help thin mucus and promote better drainage.
5. Rest: Getting plenty of rest allows the body to focus on fighting the infection and can help speed up the healing process.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Acute Suppurative Otitis Media
While mild cases of acute suppurative otitis media can often be managed at home, there are situations where seeking immediate medical attention is necessary. It is important to be aware of the following warning signs:
1. Severe pain: If the pain becomes unbearable or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as high fever or severe headache, immediate medical attention is warranted.
2. Worsening symptoms: If the symptoms worsen despite home remedies or over-the-counter medication, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
3. Symptoms in young infants: Infants under three months old with suspected acute suppurative otitis media should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
4. Persistent symptoms: If the symptoms persist for more than a few days or recur frequently, medical evaluation is necessary to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Early intervention is crucial to prevent complications and ensure a swift recovery. If you are unsure whether to seek medical attention, it is best to err on the side of caution and consult with a healthcare professional.
VIII. Treatment Options for Acute Suppurative Otitis Media
Antibiotics: When are they necessary?
The use of antibiotics in treating ASOM depends on the severity of symptoms and the presence of specific risk factors.
Healthcare providers carefully assess each case to determine the appropriate course of action.
Antibiotics may be prescribed to manage bacterial infections and prevent complications. It is vital to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed.
Pain management techniques
To alleviate the discomfort associated with ASOM, various pain management techniques can be employed.
These may include over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, applied warm compresses, or ear drops.
It is essential to follow the dosage instructions and consult a healthcare provider if the pain persists or worsens.
Surgical intervention in severe cases
In severe cases of ASOM, surgical intervention may be considered.
This can involve a procedure called a myringotomy, in which a small incision is made in the eardrum to drain any accumulated fluid or pus.
This procedure can provide relief and reduce the risk of complications.
IX. Complications Associated with Acute Suppurative Otitis Media
ASOM, if left untreated or poorly managed, can lead to potential complications.
These may include chronic otitis media, hearing loss, speech and language delays, balance problems, and the formation of a cholesteatoma.
It is crucial for parents to be aware of these potential complications and seek appropriate medical intervention.
X. How to Support a Child with Acute Suppurative Otitis Media
Comforting strategies for pain relief
Parents can employ various strategies to offer comfort and alleviate their child’s pain during ASOM.
These may include
- Creating a comforting environment
- Engaging in soothing activities
- Providing gentle massages near the affected ear
- Offering distraction through age-appropriate play or entertainment
If the child has pain without active discharge then it’s best to follow the following instructions to prevent ear drum rupture
- Never forcefully blow to your ear
- Avoid swimming
- Use ear plugs while bathing
- Avoid going to high altitude places or very tall buildings as pressure difference can cause Barotrauma.
- Cover your ear when in highly windy area
Communicating with healthcare providers
Open and effective communication with healthcare providers is essential for parents of children with ASOM.
Discussing concerns, seeking clarifications, and actively participating in treatment decisions can help ensure the best possible care for the child.
Building a supportive relationship with the healthcare team fosters confidence and empowers parents in managing ASOM.
XI. Impact of Acute Suppurative Otitis Media on Hearing
Temporary vs. permanent hearing loss
ASOM can lead to temporary hearing loss due to the accumulation of fluid or pus in the middle ear.
Prompt treatment and resolution of the infection often restore normal hearing.
However, chronic or recurrent cases of ASOM can result in long-term or permanent hearing loss, underscoring the importance of early intervention and diligent management.
Rehabilitation options for hearing impairment
If hearing loss persists or becomes permanent due to ASOM, various rehabilitation options are available.
These may include the use of hearing aids.
Consulting with an audiologist or hearing healthcare professional can help determine the most appropriate form of intervention.
XII. The Role of Allergies in Acute Suppurative Otitis Media
Connection between allergies and ASOM
Allergies can contribute to the development of ASOM, most commonly through the inflammation and swelling of the Eustachian tube caused by allergic rhinitis.
This obstruction can impair proper drainage, creating a favorable environment for bacterial growth and subsequent infection.
Managing allergies to prevent ASOM
Managing allergies effectively can help prevent ASOM and its associated complications.
This may involve identifying and avoiding allergens, utilizing nasal corticosteroid sprays or antihistamines as prescribed by a healthcare provider, and implementing measures to minimize exposure to triggers, such as dust mites or pollen.
XIII. ASOM and School Attendance
Guidelines for parents regarding school attendance
Parents of children with ASOM should follow specific guidelines regarding school attendance to prevent the spread of infection and ensure the child’s well-being.
It is crucial to keep the child at home during the acute phase of the infection, share information with school staff, and adhere to any relevant school policies or recommendations.
School accommodations for children with ASOM
Schools should provide accommodations for children with ASOM to support their educational experience.
These may include
- Excusing absences during periods of illness,
- Implementing appropriate hygiene practices,
- Providing classroom amplification systems for hearing-impaired students
- Facilitating educational support or services as required.
XIV. FAQs about Acute Suppurative Otitis Media
Can ASOM be prevented entirely?
While it may not always be entirely preventable, there are measures to reduce the risk
Can swimming cause ASOM?
Yes, swimming, particularly in water that is contaminated, can contribute to the development of Acute Otitis Media (AOM) or Acute Suppurative Otitis Media (ASOM).
Is ASOM contagious?
Acute Suppurative Otitis Media (ASOM), commonly referred to as a middle ear infection with the presence of pus, is typically caused by bacteria. While the infection itself is not directly contagious, the bacteria responsible for ASOM can be transmitted from person to person.
Can breastfeeding reduce the risk of ASOM?
Yes, breastfeeding has been associated with a reduced risk of Acute Suppurative Otitis Media (ASOM) in infants. Breast milk provides essential nutrients and antibodies that help strengthen a baby’s immune system. The antibodies in breast milk can offer protection against infections, including those that might lead to ear infections.
Research suggests that exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months of life can contribute to a lower incidence of ear infections, including ASOM. The act of breastfeeding itself also helps to ensure proper drainage of fluids from the baby’s ears.
Are there any dietary recommendations for children with ASOM?
While there isn’t a specific dietary plan for children with Acute Suppurative Otitis Media (ASOM), maintaining a balanced and healthy diet can contribute to overall well-being and may indirectly support the immune system.
How long does it take for ASOM to resolve without treatment?
The duration for Acute Suppurative Otitis Media (ASOM) to resolve without treatment can vary widely from individual to individual. In some cases, the body’s immune system may be able to clear the infection on its own, but this depends on factors such as the severity of the infection, the age and overall health of the person, and the specific bacteria involved.
In general, mild cases of ASOM may start to improve within a few days, while more severe cases may take longer. However, it’s important to note that leaving ASOM untreated can lead to complications, such as the spread of infection, hearing loss, or the development of chronic ear problems.
It’s highly advisable to seek medical attention if you suspect ASOM, especially in children or if symptoms are persistent or worsening. A healthcare professional can accurately diagnose the condition and recommend appropriate treatment, which may include antibiotics if the infection is bacterial.
XV. Conclusion
Early detection and prompt treatment of Acute Suppurative Otitis Media are paramount for managing this common childhood condition.
Equipping parents with knowledge about the causes, symptoms, preventive measures, and treatment options empowers them to navigate ASOM confidently.
By partnering with healthcare providers and staying vigilant, parents can ensure the well-being and healthy development of their children.
Related content
The Silent Battle: Understanding Serous Otitis media in children