Introduction
Tinnitus is a condition characterized by the perception of ringing, buzzing, or other phantom noises in the ears or head, without any external sound source.
It affects millions of people worldwide, making it an issue of significant concern for public health.
The constant presence of these sounds can have a profound impact on an individual’s quality of life, affecting their ability to concentrate, sleep, and communicate effectively.
Therefore, raising awareness and understanding about tinnitus is crucial to support those who are affected by it.
What Causes Tinnitus?
Tinnitus can have both neurological and external triggers.
- Idiopathic
- External factors such as exposure to loud noises, whether from occupational hazards or recreational activities, can lead to noise induced hearing loss which in turn trigger tinnitus.
- Ear wax
- Middle ear infections
- Certain medications with ototoxic properties, such as some antibiotics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Several medical conditions, including
- Temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ)
- Ménière’s diseases
Types of Tinnitus
Tinnitus can be categorized into different types based on the nature of the sounds experienced by individuals.
Subjective tinnitus
It is the most common type, where only the person affected can hear the phantom noise.
Objective tinnitus,
On the other hand, can be heard by others, and can often be attributed to underlying physical abnormalities, such as muscle contractions or blood flow irregularities.
Pulsatile tinnitus
In some cases, individuals with tinnitus may experience, characterized by rhythmic, pulsing sounds synchronized with the heartbeat.
Additionally, a fascinating phenomenon known as musical hallucinations can occur in tinnitus, where the perceived phantom noise resembles familiar tunes or songs.
Symptomatology of Tinnitus
The phantom noises experienced by individuals with tinnitus can manifest in various forms, including
- Ringing
- Buzzing
- Hissing
- Roaring
- Clicking sounds
The intensity and frequency of these sounds can also vary, with some individuals reporting intermittent episodes, while others are plagued by a constant bombardment of noise.
In addition to the auditory sensations, tinnitus can be accompanied by physical sensations such as ear fullness, pressure, or pain.
The psychological effects of tinnitus are also noteworthy, often leading to
- Emotional distress
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Irritability
- Difficulties with concentration and sleep.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
- To diagnose tinnitus, healthcare professionals typically begin by taking a thorough medical history and conducting a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s symptoms.
- Audiological tests may be employed to assess hearing abilities and identify any associated hearing loss.
- Pure-tone audiometry
- Tympanometry,

- Imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be utilized to rule out any structural abnormalities in the auditory system.
It is important to differentiate tinnitus from other auditory disorders, such as hyperacusis (extreme sensitivity to sound) or misophonia (negative emotional response to specific sounds), to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options
Various treatment options are available to manage tinnitus and provide relief to those affected.
- Sound therapy, utilizing external sounds such as white noise or natural sounds to mask or distract from the phantom noise, can be effective in reducing the perception of tinnitus.
- Masking devices, worn like hearing aids, can provide sound enrichment and amplify ambient noise to alleviate the focus on tinnitus.
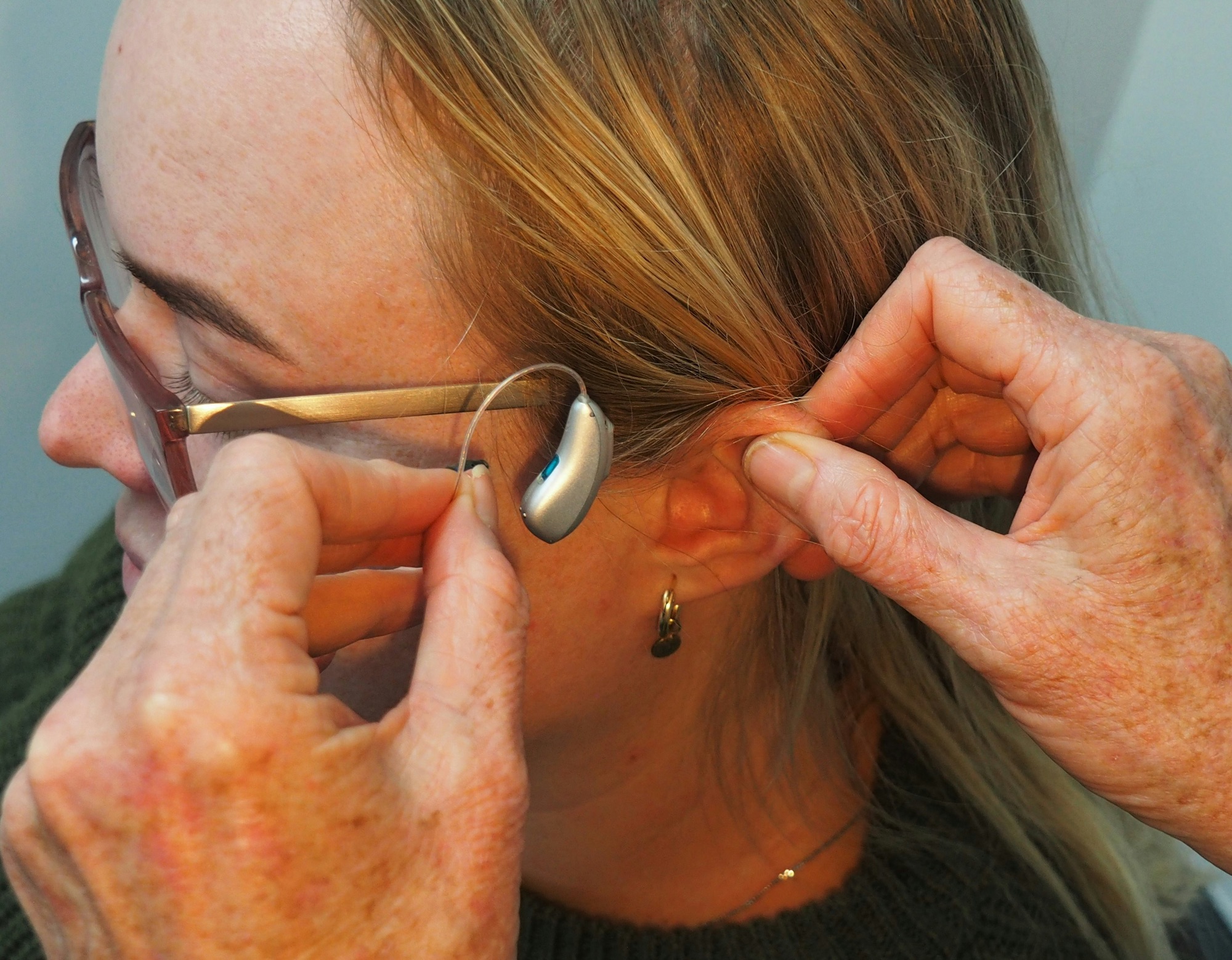
- Tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT) takes a comprehensive approach involving counseling and sound therapy to help individuals habituate to the phantom noise and reduce its impact on their lives.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can also be employed to address any negative thought patterns and emotional distress associated with tinnitus.
- Medications and supplements, although not universally effective, can provide some relief for individuals with tinnitus.
These may include
- Antidepressants
- Anticonvulsants
- Supplements such as Ginkgo biloba, zinc, or melatonin.
Additionally, numerous investigational treatments and emerging technologies, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) or auditory nerve stimulation, show promise in the field of tinnitus research.
Coping Strategies for Tinnitus
While there is no definitive cure for tinnitus, implementing coping strategies can help individuals manage and alleviate the impact of tinnitus on their daily lives.
- Stress management techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or engaging in activities that promote relaxation and mindfulness, can contribute to overall well-being.
- Support groups and counseling services provide valuable platforms for individuals with tinnitus to share experiences, gain emotional support, and learn coping strategies from others facing similar challenges.
- Additionally, optimizing sleep hygiene through strategies like maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a quiet and calming sleep environment,
- Using white noise machines can help manage tinnitus-related insomnia.
Prevention of Tinnitus
Prevention plays a crucial role in minimizing the risk of developing tinnitus.
- Protecting hearing abilities by wearing earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments, such as concerts or construction sites, can significantly reduce the likelihood of noise-induced tinnitus.
- Workplace safety regulations and guidelines should be strictly adhered to, ensuring that employees are provided with adequate protection against occupational hazards that can lead to tinnitus.
- Responsible use of medications and avoiding exposure to ototoxic substances can prevent medication-induced tinnitus.
Individuals should consult healthcare professionals regarding potential ototoxic effects and understand the risks associated with specific medications or substances.
Tinnitus in Children and Adolescents
Tinnitus is not limited to adults; it can also affect children and adolescents.
The prevalence of tinnitus in this population is relatively low but can pose unique challenges due to cognitive and developmental factors.
Tinnitus can have a significant impact on communication and learning abilities, potentially affecting academic performance and social interactions.
Management strategies for tinnitus in children and adolescents often involve a multidisciplinary approach,
- Audiological assessments
- Counseling
- Educational support
It is crucial to provide resources and a supportive environment to aid in the management of tinnitus-related difficulties in this age group.
Tinnitus Research and Advancements
Ongoing research into tinnitus aims to unravel its underlying mechanisms and discover new interventions for its management.
Promising avenues of scientific investigation include neuroplasticity and neuromodulation techniques, targeting specific brain regions involved in auditory processing.
Emerging technologies, such as
- Cochlear implants
- Bimodal stimulation
- Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS)
- Deep brain stimulation (DBS)
Tinnitus and Mental Health
The link between tinnitus and mental health is well-documented, with tinnitus often co-occurring with anxiety, depression, and cognitive issues.
Addressing these mental health aspects is essential in comprehensive tinnitus management.
Holistic approaches that integrate psychological interventions, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, with sound-based therapy options can significantly improve the overall well-being of individuals dealing with tinnitus.
Summary
In summary, tinnitus is a prevalent condition characterized by the perception of phantom noises in the absence of external sounds.
Understanding its causes, types, symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial in supporting individuals affected by tinnitus.
By empowering individuals with knowledge and breaking the stigma surrounding tinnitus, we can foster a compassionate and supportive environment for those dealing with this constant racket.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A. Can tinnitus lead to complete hearing loss?
Tinnitus itself does not directly cause complete hearing loss.
However, underlying conditions or exposures that contribute to tinnitus, such as severe noise-induced hearing loss or certain medical conditions, may have the potential to lead to hearing loss.
B. Is tinnitus a sign of an underlying medical condition?
Tinnitus can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as
- sensorineural hearing loss
- Circulatory problems
- Temporomandibular joint disorder
It is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine if further evaluation is necessary.
C. Can tinnitus be cured?
As of now, there is no known cure for tinnitus. However, various management strategies and treatment options can help individuals reduce the impact of tinnitus on their quality of life.
D. How does tinnitus impact sleep?
Tinnitus can disrupt sleep patterns, making it difficult for individuals to fall asleep or stay asleep.
Additionally, the constant noise can cause anxiety and stress, which further aggravate sleep disturbances.
E. Are there any home remedies for tinnitus relief?
While there is no guaranteed home remedy for tinnitus relief, some individuals report finding temporary relief through techniques such
- White noise machines
- Practicing relaxation exercises
- Avoiding triggers such as caffeine or nicotine
It is important to consult a healthcare professional before attempting any home remedies.
